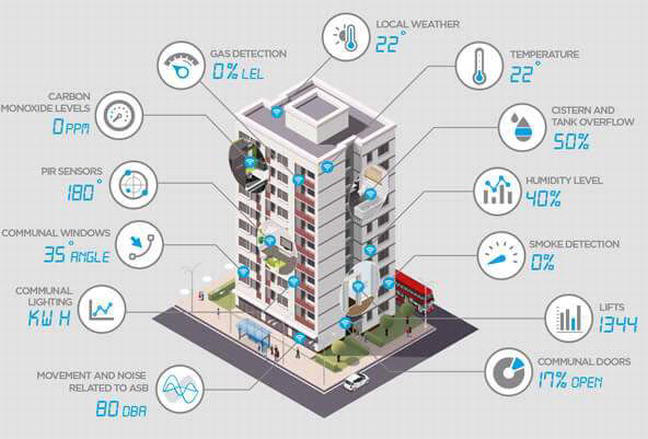
Smart buildings are an emerging trend in modern architecture that seamlessly integrates technology to enhance building performance, improve energy efficiency, and create more comfortable living and working environments. With rapid advancements in technology, buildings are no longer just physical structures; they are becoming intelligent systems capable of optimizing everything from lighting and temperature to security and energy consumption.
As someone who has observed the evolution of architecture and technology, I’m fascinated by how these innovations are changing the way we interact with the spaces we inhabit. In this article, we’ll dive into the concept of smart buildings, explore the technologies involved, and examine the benefits of integrating these systems into modern architectural designs.
What Makes a Building “Smart”?

1. Technology Integration
At the core of a smart building is its use of advanced technologies that monitor, control, and automate various systems within the structure. These technologies include sensors, automated controls, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which work together to create a responsive and efficient environment.
For example, a smart thermostat that adjusts the temperature based on occupancy and weather conditions can help conserve energy by ensuring heating or cooling is only used when needed. Similarly, smart lighting systems can automatically dim or brighten based on room occupancy or the time of day, reducing energy consumption.
Key Technologies in Smart Buildings:
-
IoT (Internet of Things): Devices connected through a network that can share data and make automated decisions.
-
Building Management Systems (BMS): Software that integrates all building systems (HVAC, lighting, security, etc.) for seamless operation.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven algorithms that can predict and optimize building performance based on usage patterns.
2. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
A major goal of smart buildings is to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Smart buildings use sensors and automation to optimize energy use, minimize waste, and promote sustainability. For instance, smart HVAC systems automatically adjust to the optimal temperature based on external weather conditions and occupancy patterns, ensuring energy isn’t wasted on heating or cooling empty rooms.
Additionally, smart buildings can integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, and use energy storage systems to manage power distribution. Green building materials and design strategies further enhance sustainability, making these buildings not only smart but environmentally friendly.
Strategies for Sustainability:
-
Energy-efficient systems: Smart lighting, heating, and cooling solutions to minimize energy consumption.
-
Solar power integration: Installing solar panels to reduce reliance on the grid.
-
Water conservation: Smart water systems that monitor usage and detect leaks to prevent waste.
3. Automation for Comfort and Convenience
Smart buildings offer automation that increases comfort and convenience for occupants. For instance, smart home systems allow users to control lighting, heating, and appliances from their smartphones or voice commands. In office buildings, automated elevators, adjustable office lighting, and intelligent meeting room scheduling ensure that spaces are used efficiently and comfortably.
These systems are not just about convenience but also about improving productivity and enhancing the overall user experience. Imagine entering a room that automatically adjusts the lighting to your preferred brightness, tunes the temperature to your comfort level, and starts your favorite music—all before you even sit down.
Examples of Smart Building Automation:
-
Voice-controlled environments: Adjusting temperature, lighting, and multimedia systems with simple voice commands.
-
Smart security systems: Facial recognition or biometric systems that provide seamless, secure access.
-
Automated cleaning systems: Robots or IoT devices that monitor air quality or detect cleaning needs in real-time.
Benefits of Smart Buildings
1. Cost Savings and Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of smart buildings is cost savings, particularly in terms of energy consumption. By using smart technology to monitor and manage energy use, buildings can reduce electricity, heating, and cooling costs. Over time, these savings can add up, making smart buildings more economical to operate than traditional buildings.
Additionally, smart buildings can help manage operational costs by streamlining building maintenance. For example, predictive maintenance systems can identify potential issues before they cause problems, preventing costly repairs and extending the life of building systems.
Key Cost Savings Areas:
-
Energy usage: Reducing electricity, water, and heating/cooling costs.
-
Maintenance: Predictive maintenance to avoid costly repairs and downtime.
-
Automation: Reducing the need for manual labor in areas like lighting, heating, and security.
2. Improved Security and Safety
Smart buildings use advanced security systems that integrate cameras, sensors, and real-time monitoring to keep the building and its occupants safe. Facial recognition, biometric scanning, and motion detectors ensure that only authorized individuals can enter certain areas. These systems can also provide immediate alerts in case of suspicious activity, enhancing overall safety.
Furthermore, smart fire detection systems can identify early signs of fire, gas leaks, or other hazards, allowing for quicker response times and minimizing the risk to residents or workers.
Examples of Smart Security:
-
24/7 surveillance: Cameras that use AI to recognize and alert staff of unusual behavior.
-
Access control: Smart locks and biometric access systems.
-
Fire and gas detection: Early warning systems that can prevent dangerous situations.
3. Health and Well-being of Occupants
In addition to energy efficiency and security, smart buildings are designed with the health and well-being of occupants in mind. Air quality sensors help ensure that indoor environments have proper ventilation, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and promoting overall wellness. Smart lighting systems can also reduce eye strain by adjusting to natural light levels and providing optimal illumination.
In office environments, smart buildings can adjust temperature, lighting, and air quality based on individual preferences or time of day to create a comfortable, productive work environment.
Health-Focused Smart Systems:
-
Air quality monitoring: Systems that regulate ventilation and humidity for better indoor air quality.
-
Lighting control: Adjusting lighting intensity and color to enhance productivity and reduce fatigue.
-
Temperature control: Ensuring comfort by optimizing temperature based on occupancy and preferences.
The Future of Smart Buildings
1. Integration with Urban Infrastructure
As cities become smarter, buildings are increasingly integrated with urban infrastructure. Smart buildings are starting to connect with transportation systems, utilities, and other infrastructure to create more cohesive urban ecosystems. This can include features such as smart traffic management that adjusts based on the building’s energy usage or linking electric vehicle charging stations to the building’s power grid for optimized energy use.
2. Sustainability and Circular Economy
The future of smart buildings is closely linked to sustainability and the growing focus on the circular economy. Future smart buildings will be designed to use less energy, reduce waste, and optimize resource consumption. These buildings will incorporate recycled materials, renewable energy sources, and efficient waste management systems to reduce their environmental footprint.
Smart buildings will continue to evolve, becoming more energy-efficient, connected, and integrated with their surroundings. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will allow these buildings to learn from their environments and continuously improve efficiency.
Conclusion: The Future of Architecture is Smart
Smart buildings represent the next evolution in modern architecture, where technology, sustainability, and efficiency work together to create better living and working environments. The integration of advanced technologies—such as IoT, AI, and automation—offers immense benefits, from reducing energy consumption and improving security to enhancing occupant comfort and health.